|
Akshat Ramachandran I am a 2nd year Ph.D student in Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE) at the Synergy Lab in the Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech) advised by Prof. Tushar Krishna. Google Scholar / CV / LinkedIn / GitHub / Email Community Service: In an effort to give back to the community, I conduct a weekly guidance session for undergraduate/graduate students. Please read the description in the form and if you feel this could benefit you, please fill out the form. (Note: On travel currently, please expect delays in response.) |

|
||||||||||
|
The central focus of my research is in the design and development of efficient and high performance algorithms, architectures and systems for accelerating emergent deep learning applications (computer vision and NLP). My research breaks down traditional barriers existing between different computing elements and adopts an interdisciplinary approach spanning the entire computing stack. To realise my vision of developing the next generation of computing systems, my interests and technical work spans a wide gamut and lies at the intersection of computer architecture, VLSI, computer arithmetic and deep learning.
|
|
|
|
|
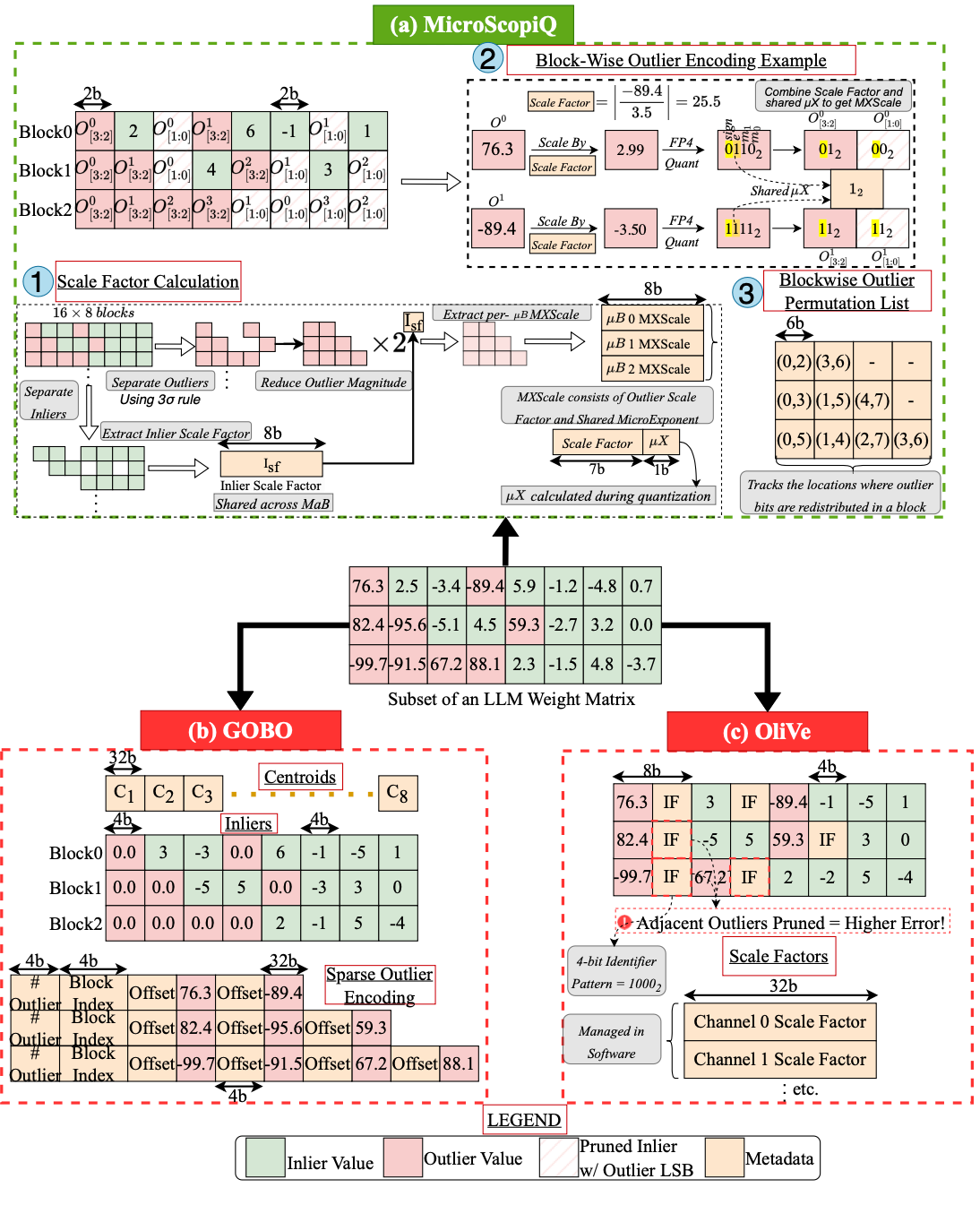
Akshat Ramachandran, Souvik Kundu, Tushar Krishna International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), 2025 Paper Quantization of foundational models (FMs) is significantly more challenging than traditional DNNs due to the emergence of large magnitude features called outliers. Existing outlier-aware algorithm/architecture co-design techniques either use mixed-precision, retaining outliers at high precision but compromise hardware efficiency, or quantize inliers and outliers at the same precision, improving hardware efficiency at the cost of accuracy. To address this mutual exclusivity, in this paper, we propose MicroScopiQ, a novel co-design technique that leverages pruning to complement outlier-aware quantization. MicroScopiQ retains outliers at higher precision while pruning a certain fraction of least important weights to distribute the additional outlier bits; ensuring high accuracy, aligned memory and hardware efficiency. We design a high-throughput, low overhead accelerator architecture composed of simple multi-precision INT processing elements and a novel network-on-chip called ReCoN that efficiently abstracts the complexity of supporting high-precision outliers. Additionally, unlike existing alternatives, MicroScopiQ does not assume any locality of outlier weights, enabling applicability to a broad range of FMs. Extensive experiments across various quantization settings show that MicroScopiQ achieves SoTA quantization performance while simultaneously improving inference performance by 3x and reducing energy by 2x over existing alternatives. |
||||||||||
|
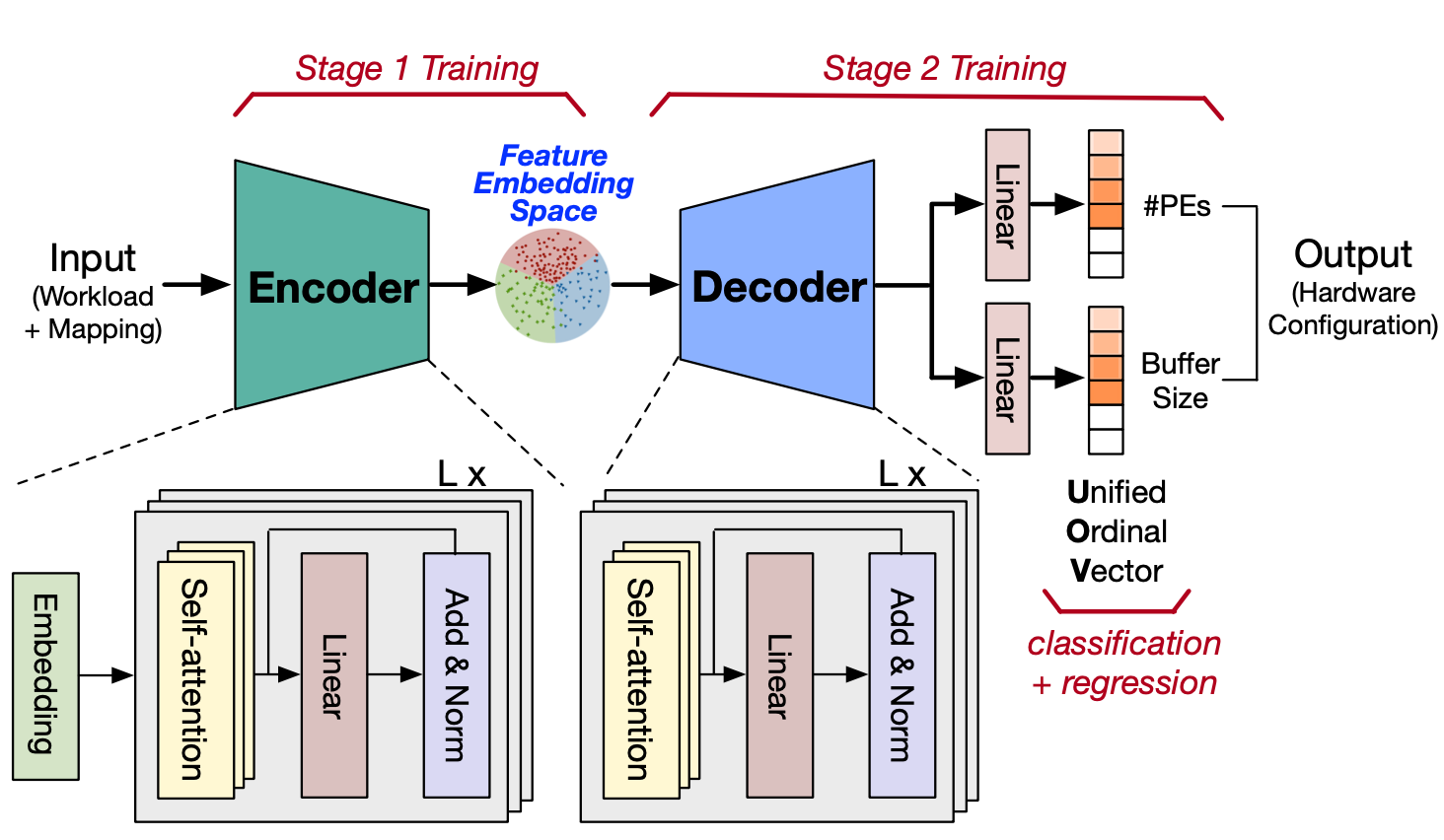
Akshat Ramachandran*, Jamin Seo*, Yu-Yuan Chang, Anirudh Itagi, Tushar Krishna *Equal Contribution Design Automation and Test in Europe (DATE), 2025 Paper Design space exploration (DSE) plays a crucial role in enabling custom hardware architectures, particularly for emerging applications like AI, where optimized and specialized designs are essential. With the growing complexity of deep neural networks (DNNs) and the introduction of advanced large language models (LLMs), the design space for DNN accelerators is expanding at an exponential rate. Additionally, this space is highly non-uniform and non-convex, making it increasingly difficult to navigate and optimize. Traditional DSE techniques rely on search-based methods, which involve iterative sampling of the design space to find the optimal solution. However, this process is both time-consuming and often fails to converge to the global optima for such design spaces. Recently, AIRCHITECT V1, the first attempt to address the limitations of search-based techniques, transformed DSE into a constant-time classification problem using recommendation networks. However, AIRCHITECT V1 lacked generalizability and had poor performance on complex design spaces. In this work, we propose AIRCHITECT V2, a more accurate and generalizable learning-based DSE technique applicable to large-scale design spaces that overcomes the shortcomings of earlier approaches. Specifically, we devise an encoder-decoder transformer model that (a) encodes the complex design space into a uniform intermediate representation using contrastive learning and (b) leverages a novel unified representation blending the advantages of classification and regression to effectively explore the large DSE space without sacrificing accuracy. Experimental results evaluated on 105 real DNN workloads demonstrate that, on average, AIRCHITECT V2 outperforms existing techniques by 15% in identifying optimal design points. Furthermore, to demonstrate the generalizability of our method, we evaluate performance on unseen model workloads and attain a 1.7x improvement in inference latency on the identified hardware architecture. |
||||||||||
|
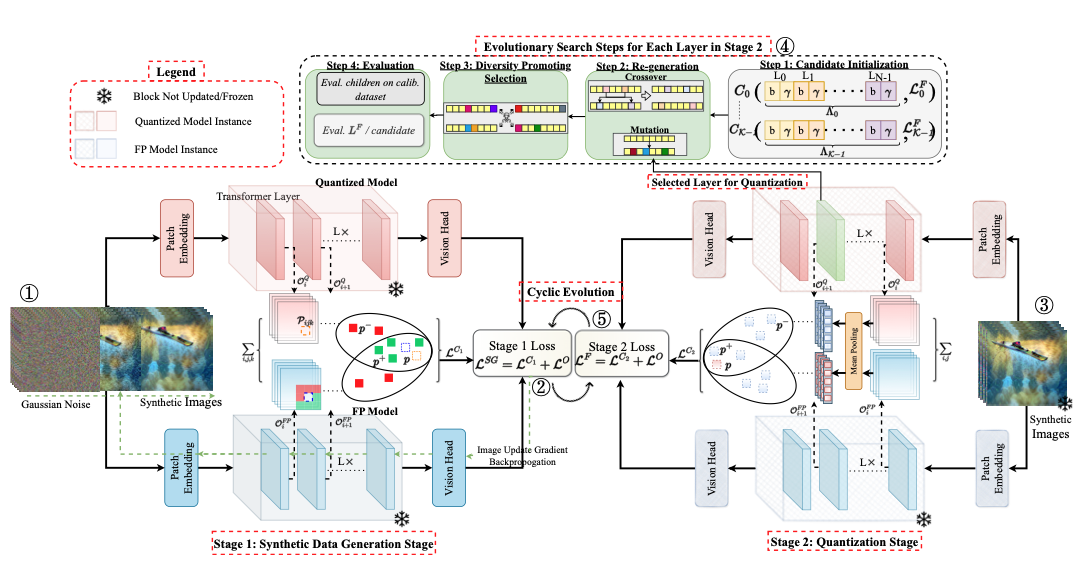
Akshat Ramachandran, Souvik Kundu, Tushar Krishna European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2024 Paper We present CLAMP-ViT, a data-free post-training quantization method for vision transformers (ViTs). We identify the limitations of recent techniques, notably their inability to leverage meaningful inter-patch relationships, leading to the generation of simplistic and semantically vague data, impacting quantization accuracy. CLAMP-ViT employs a two-stage approach, cyclically adapting between data generation and model quantization. Specifically, we incorporate a patch-level contrastive learning scheme to generate richer, semantically meaningful data. Furthermore, we leverage contrastive learning in layer-wise evolutionary search for fixed- and mixed-precision quantization to identify optimal quantization parameters while mitigating the effects of a non-smooth loss landscape. Extensive evaluations across various vision tasks demonstrate the superiority of CLAMP-ViT, with performance improvements of up to 3% in top-1 accuracy for classification, 0.6 mAP for object detection, and 1.5 mIoU for segmentation at similar or better compression ratio over existing alternatives. |
||||||||||
|
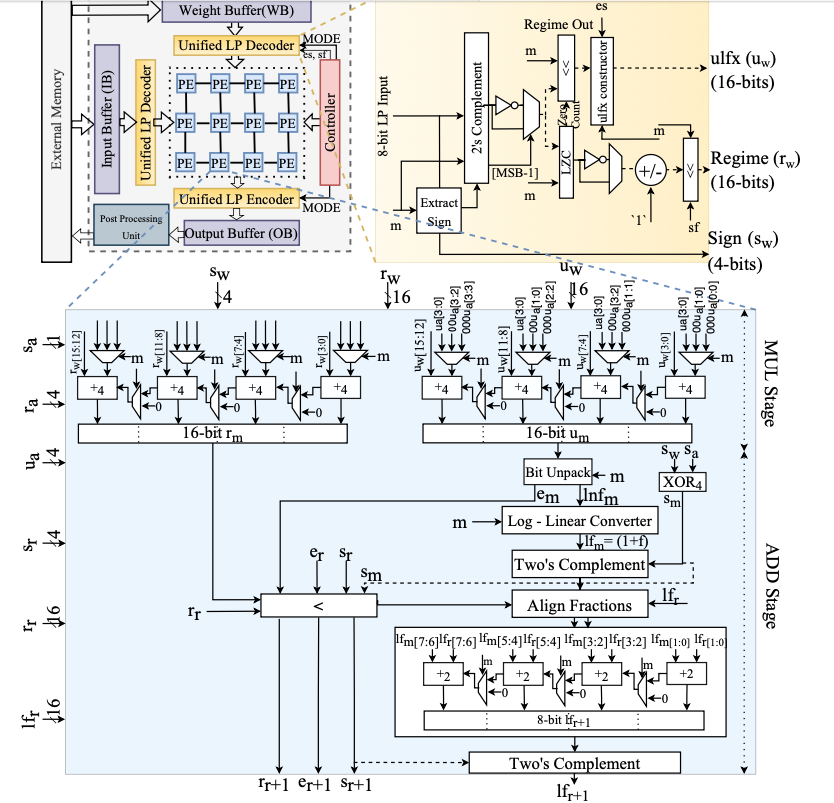
Akshat Ramachandran, Zishen Wan, Geonhwa Jeong, John Gustafson, Tushar Krishna ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), 2024 Paper We present Logarithmic Posits (LP), a novel adaptive data type for Deep Neural Network (DNN) quantization, offering significant efficiency and accuracy improvements. Our approach, LP Quantization (LPQ), optimizes DNN parameters using a genetic algorithm, closely preserving model accuracy with a specialized objective. The resulting LP accelerator architecture (LPA) doubles performance per area and improves energy efficiency by 2.2x over traditional quantization methods, with minimal accuracy loss. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
Last Update: Apr. 2025
|









